Buyer Login
Injection and Infusion are two common methods used to administer medications or fluids directly into the body, typically via the bloodstream. They differ mainly in how the substance is delivered and over what period of time. An injection is the act of delivering a substance into the body using a syringe and needle.
💉 Examples :
Vaccines (IM or SC)
Insulin (SC)
Pain medications (IM or IV)
(a) Intravenous (IV) – Into a vein (fastest effect). (b) Intramuscular (IM) – Into a muscle. (c) Subcutaneous (SC) – Into the layer under the skin. (d) Intradermal (ID) – Into the skin layer.
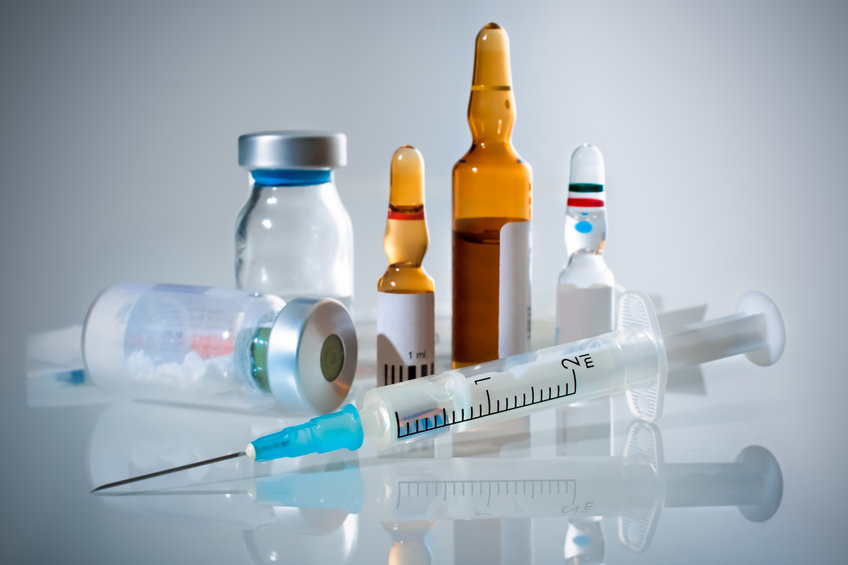
Injection and Infusion are two common methods used to administer medications or fluids directly into the body, typically via the bloodstream. They differ mainly in how the substance is delivered and over what period of time. An injection is the act of delivering a substance into the body using a syringe and needle.
💉 Examples :
Vaccines (IM or SC)
Insulin (SC)
Pain medications (IM or IV)
(a) Intravenous (IV) – Into a vein (fastest effect). (b) Intramuscular (IM) – Into a muscle. (c) Subcutaneous (SC) – Into the layer under the skin. (d) Intradermal (ID) – Into the skin layer.
Tablet is a solid, compressed form of medication, typically flat or oval-shaped, made by pressing powdered ingredients together.
💊 Examples :
Paracetamol tablets
Aspirin
Metformin
Uncoated – plain and quickly dissolves.
Film-coated – easier to swallow, masks taste.
Enteric-coated – designed to dissolve in the intestine, not the stomach.
Chewable – meant to be chewed before swallowing.
Effervescent – dissolved in water before ingestion.
Extended-release (ER, SR, XR) – releases drug over time.
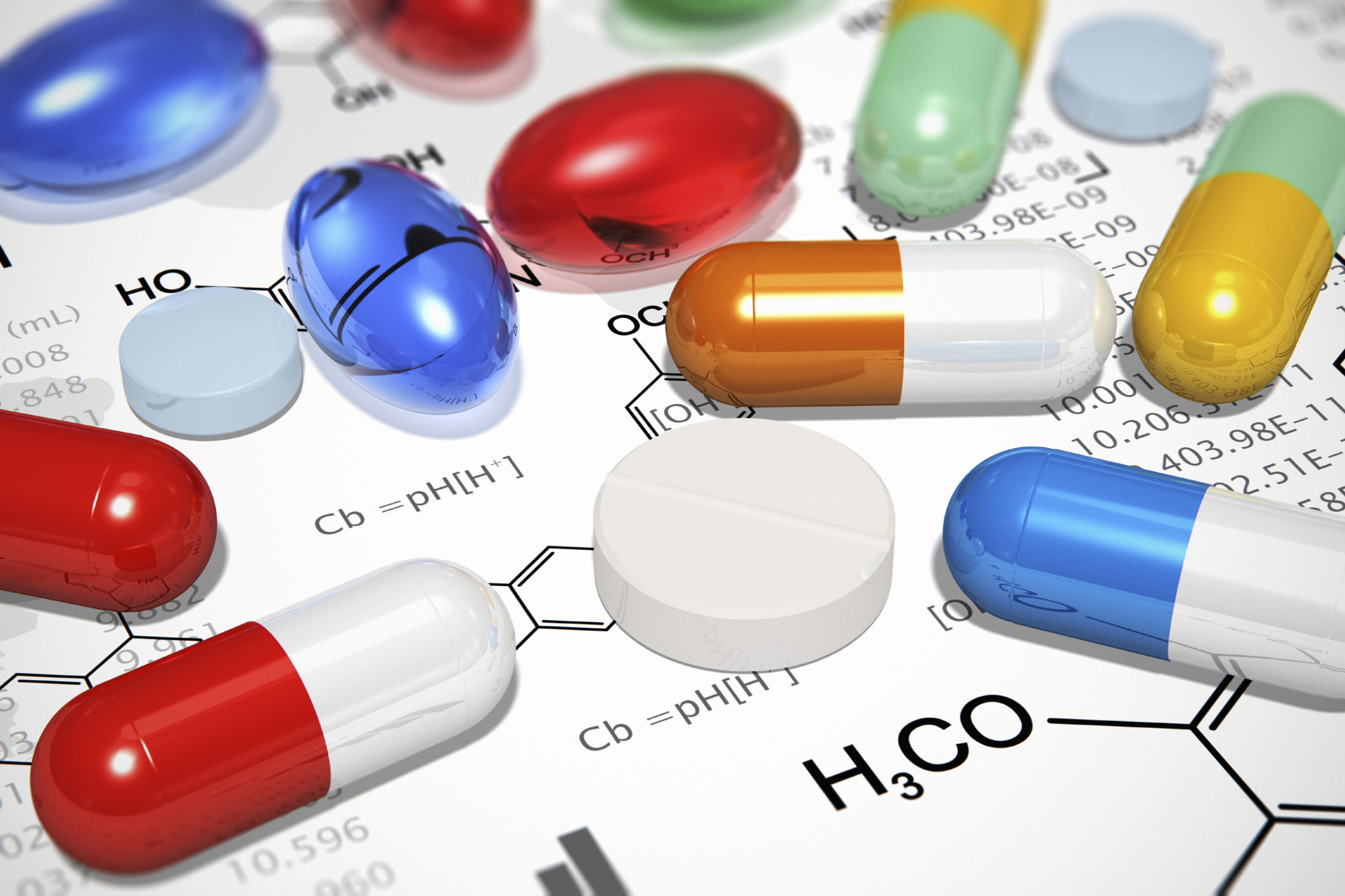
Tablet is a solid, compressed form of medication, typically flat or oval-shaped, made by pressing powdered ingredients together.
💊 Examples :
Paracetamol tablets
Aspirin
Metformin
Uncoated – plain and quickly dissolves.
Film-coated – easier to swallow, masks taste.
Enteric-coated – designed to dissolve in the intestine, not the stomach.
Chewable – meant to be chewed before swallowing.
Effervescent – dissolved in water before ingestion.
Extended-release (ER, SR, XR) – releases drug over time.
Syrups and Suspensions, two common liquid oral dosage forms used especially in pediatric and elderly care. A syrup is a concentrated aqueous (water-based) solution of sugar (usually sucrose) containing dissolved medications.
💧 Examples:
Paracetamol syrup
Cough syrups (e.g., dextromethorphan)
Antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine)
Clear, homogeneous liquid (no particles).
Sweet taste – masks bitter medication.
Drug is completely dissolved in the liquid.
No need to shake before use.
Stable if stored properly.
May contain preservatives, flavoring, and coloring agents.
Pleasant taste → good for children.
Uniform dose in each spoonful.
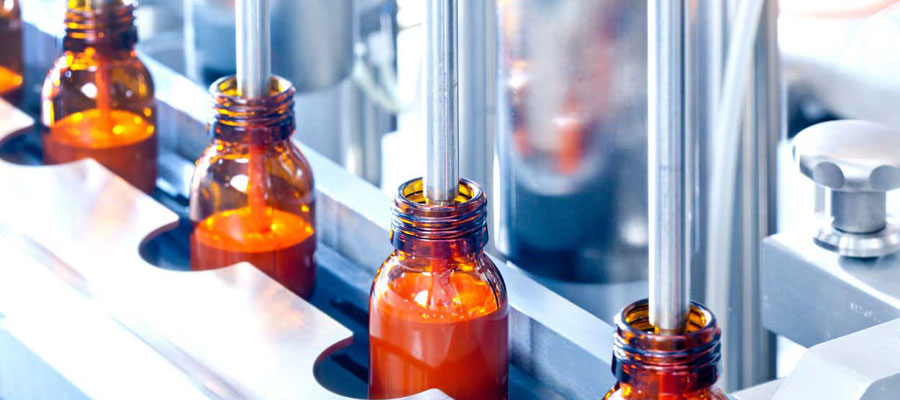

Syrups and Suspensions, two common liquid oral dosage forms used especially in pediatric and elderly care. A syrup is a concentrated aqueous (water-based) solution of sugar (usually sucrose) containing dissolved medications.
💧 Examples:
Paracetamol syrup
Cough syrups (e.g., dextromethorphan)
Antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine)
Clear, homogeneous liquid (no particles).
Sweet taste – masks bitter medication.
Drug is completely dissolved in the liquid.
No need to shake before use.
Stable if stored properly.
May contain preservatives, flavoring, and coloring agents.
Pleasant taste → good for children.
Uniform dose in each spoonful.
Overview of medical instruments, which are essential tools used by healthcare professionals to diagnose, monitor, and treat patients. They range from simple hand-held tools to complex machines.
1. Diagnostic Instruments :
|
Stethoscope |
Listening to heart, lung, and bowel sounds |
|
Thermometer |
Measuring body temperature |
|
Sphygmomanometer |
Measuring blood pressure |
|
Otoscope |
Examining ears |
|
Ophthalmoscope |
Examining eyes |
|
Tongue depressor |
Holding down the tongue to view the throat |
|
ECG (Electrocardiogram) |
Monitoring heart electrical activity |
|
Scalpel |
Making incisions (surgical knife) |
|
Forceps |
Grasping or holding tissue |
|
Hemostat |
Controlling bleeding (clamps blood vessels) |
|
Retractors |
Holding back tissues or organs |
|
Scissors |
Cutting tissues or sutures |
|
Needle holder |
Holding needles for suturing |
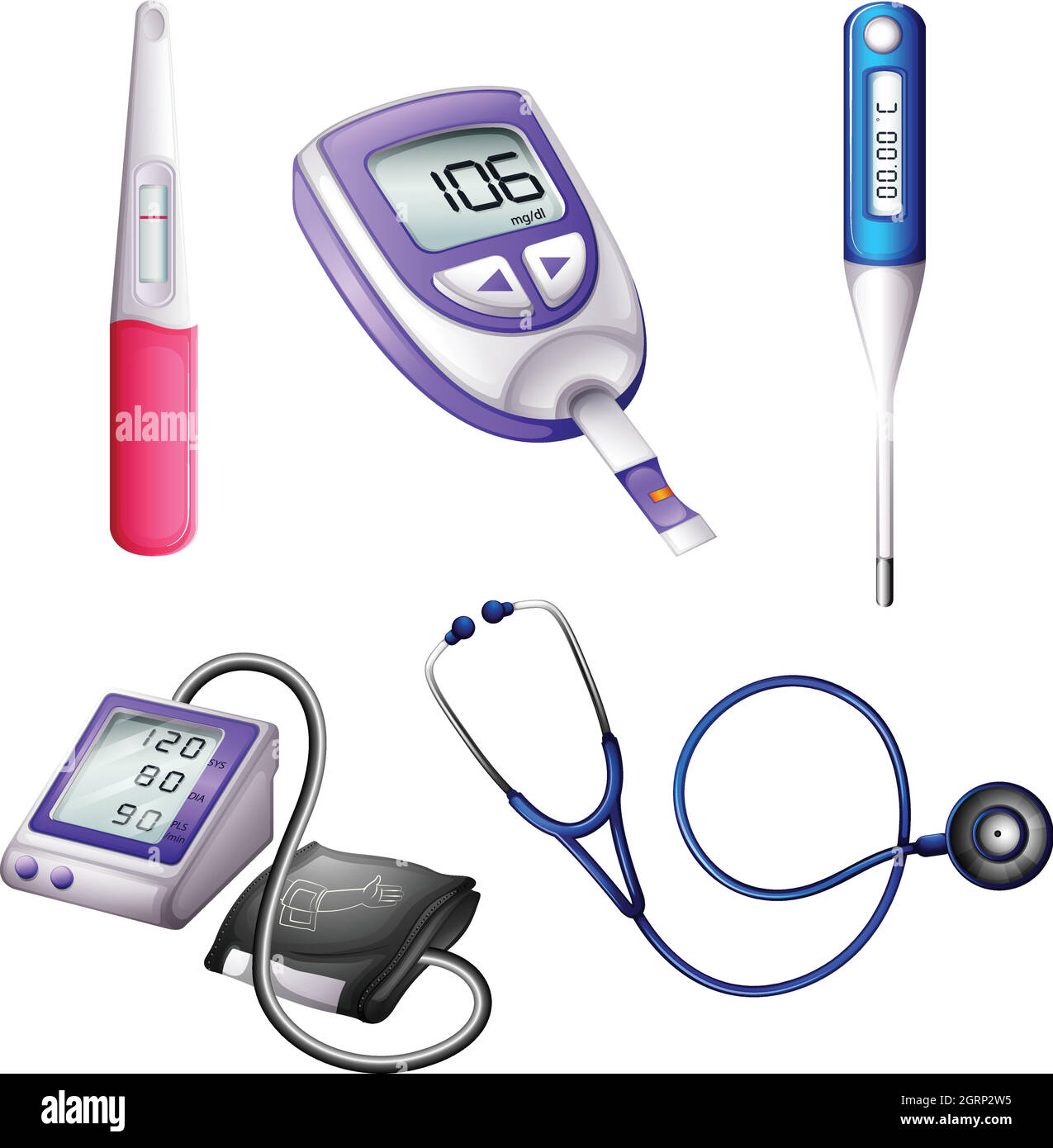
Overview of medical instruments, which are essential tools used by healthcare professionals to diagnose, monitor, and treat patients. They range from simple hand-held tools to complex machines.
1. Diagnostic Instruments :
|
Stethoscope |
Listening to heart, lung, and bowel sounds |
|
Thermometer |
Measuring body temperature |
|
Sphygmomanometer |
Measuring blood pressure |
|
Otoscope |
Examining ears |
|
Ophthalmoscope |
Examining eyes |
|
Tongue depressor |
Holding down the tongue to view the throat |
|
ECG (Electrocardiogram) |
Monitoring heart electrical activity |
|
Scalpel |
Making incisions (surgical knife) |
|
Forceps |
Grasping or holding tissue |
|
Hemostat |
Controlling bleeding (clamps blood vessels) |
|
Retractors |
Holding back tissues or organs |
|
Scissors |
Cutting tissues or sutures |
|
Needle holder |
Holding needles for suturing |